veterinary online-physiology of DIGESTION
SALIVARY GLAND
TYPES OF SALIVARY GLAND
1-serous salivary gland: secretion in thin and watery as parotid salivary gland
2-mucous salivary gland: secretion is thick and mucous as sublingual salivary gland
3-mixed salivary gland: secretion is mixed as submaxillary salivary gland
3-it is considered as excretory pass way
4-it has antiseptic action
5-regulate body temperature
6-saliva has buffering action
7-in ruminant it is alkaline so it neutralize acid in rumen
8-cooling of hot food and dilute irritant substance
9-cleaning mouth from food
10-moisten of food to help mastication and swallowing
11-help speech
regulation of saliva formation it is controlled by both sympathatic and parasympathatic
1-stimulation of parasympathatic : true secretion and very large amount rich in electrolytes but poor in enzymes
2-stimulation of sympathatic : little viscus amount of secretion rich in enzymes but poor in electrolytes also lead to contraction of smooth muscle around gland lead to release saliva
 |
| salivary gland |
3-mixed salivary gland: secretion is mixed as submaxillary salivary gland
function of saliva gland
1-play good role in water balance
2-contain alpha amylase enzyme3-it is considered as excretory pass way
4-it has antiseptic action
5-regulate body temperature
6-saliva has buffering action
7-in ruminant it is alkaline so it neutralize acid in rumen
8-cooling of hot food and dilute irritant substance
9-cleaning mouth from food
10-moisten of food to help mastication and swallowing
11-help speech
regulation of saliva formation it is controlled by both sympathatic and parasympathatic
1-stimulation of parasympathatic : true secretion and very large amount rich in electrolytes but poor in enzymes
2-stimulation of sympathatic : little viscus amount of secretion rich in enzymes but poor in electrolytes also lead to contraction of smooth muscle around gland lead to release saliva
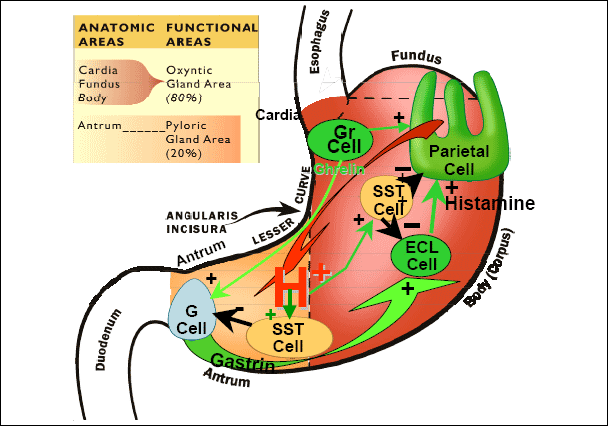
GASTRIC SECRETION
types of gastric gland
1-G cell : secrete gastrin hormone
2-peptic cell : secrete pepsin
3-mucous cell : secrete gastric HCL and intrinsic factor
4-endocrine paracrine : secrete histamine and somatostatin
5-argentaffin cell : secrete serotonin
control of gastric secretion by two mechanisms (neural and hormonal) and divided into 3 phases:
1-cephalic phase : its neural controlled by two reflexes (conditioned and unconditioned )
2-gastric phase
3-intestinal phase : its stimulated by (secretagogues) and inhibited by (enterogastrones and enterogastric reflex)
4-endocrine paracrine : secrete histamine and somatostatin
5-argentaffin cell : secrete serotonin
control of gastric secretion by two mechanisms (neural and hormonal) and divided into 3 phases:
1-cephalic phase : its neural controlled by two reflexes (conditioned and unconditioned )
2-gastric phase
3-intestinal phase : its stimulated by (secretagogues) and inhibited by (enterogastrones and enterogastric reflex)